How is Income Tax Calculated and How Does an Income Tax Calculator Help?

An income tax calculator is a digital tool you can use to calculate your tax payment for the relevant financial year. It factors in variables such as your total income, age, deductions, and home loan payments, and assesses your tax liability instantly. It is a powerful tool because tax calculations can be complex as there are many tax laws involved. Simply arriving at your taxable income can be challenging. Nevertheless, an income tax calculator generates error-free results in moments. To know how it works, learn about how income tax is calculated in India.
How is income tax calculated in India?
Income tax is calculated based on two key factors: your taxable income and the tax slab applicable. However, since Union Budget 2019-20, another factor to consider is the tax regime you choose. Your taxable income and tax slabs are subject to change based on which regime you pick.
Old regime
Under the old tax regime, you arrive at your taxable income by adding your income under salary, capital gains, house property, business/profession, and other sources and subtracting deductions under Chapter VI, such as Section 80C and 80D, among others, and exemptions such as HRA and LTA. When you use an income tax calculator, you need to input a few values, and all of this is done behind the scenes. Next, your taxable income is taxed at the old tax slab rates. Depending on your age and taxable income, the relevant tax slab rate will apply.
New regime
Under the new tax regime, you forego most exemptions and deductions. In which case, you simply need to add your income from salary, capital gains, house property, business/ profession, and other sources and subtract certain permissible deductions to obtain your taxable income. This is then taxed as per the applicable tax slab rate. The new tax slab rates are concessional, that is, they are often lower across various income categories.
What are the income tax slabs?
Old regime
For individual taxpayers below age 60
|
Taxable Income |
Tax Rates |
|---|---|
|
Up to |
NIL |
|
|
5% of income above |
|
|
|
|
Above |
|
For senior citizen taxpayers – between 60 and 80 years
|
Taxable Income |
Tax Rates |
|---|---|
|
Up to |
NIL |
|
|
5% of income above |
|
|
|
|
Above |
|
For super-senior citizen taxpayers – aged 80 and above
|
Taxable Income |
Tax Rates |
|---|---|
|
Up to |
NIL |
|
|
20% of income above |
|
Above |
|
New regime
|
Taxable Income |
Tax Rates |
|---|---|
|
Up to |
NIL |
|
|
5% of income above |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Above |
|
*4% cess on income tax is applicable on all the above.
What is the non-taxable income limit?
As per the old regime, you are exempt from tax if your taxable income does not exceed 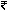 2.5 Lakhs if you are a regular citizen,
2.5 Lakhs if you are a regular citizen, 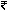 3 Lakhs if you are a senior citizen, and
3 Lakhs if you are a senior citizen, and 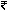 5 Lakhs if you are a super-senior citizen. In case of the new regime, irrespective of age, the non-taxable limit is
5 Lakhs if you are a super-senior citizen. In case of the new regime, irrespective of age, the non-taxable limit is 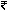 2.5 Lakhs.
2.5 Lakhs.
Nonetheless, there is a rebate up to 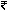 12,500 offered under Section 87A if your taxable income does not exceed
12,500 offered under Section 87A if your taxable income does not exceed 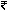 5 Lakhs. So, under both regimes, zero income tax may be paid if your taxable income does not cross
5 Lakhs. So, under both regimes, zero income tax may be paid if your taxable income does not cross 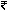 5 Lakhs.
5 Lakhs.
How to use an income tax calculator for AY 2021-22?
Firstly, open an income tax calculator online. Then:
- Pick taxpayer category
- Pick your age bracket
- Disclose your annual income (salary, other sources, etc.)
- Indicate eligible deductions/ exemptions, such as:
- HRA and LTA
- 80E (Education loan interest)
- 80C (PPF, ELSS, home loan principal, etc.)
- 24B (Home loan interest)
*Enter ‘0’ for fields that are not applicable.
To claim home loan tax deductions, keep your home loan certificate ready. With offerings such as the Bajaj Housing Finance Limited Home Loan, you can download your certificate from the digital customer portal. Here, you also enjoy ample finance with a flexible tenor and attractive interest rates.
Now that you know how an income tax calculator aids tax planning, pledge to be more tax-efficient in the years to come.
