News >> Technology >>
Impacts of key trends in Indian telecom industry
By R. Krishna Kumar
|
Saturday, 10 June 2006, 19:30 IST
Indian telecom industry is going through a phenomenal growth in the past five years. Many trends that shaped the direction of this industry have emerged during this period. This article discusses the key trends in the Indian telecom industry, its driver and the major impact of such trends affecting the operators, vendors and customers.
1.People go wireless: Indian customers are embracing the mobile technology in a big way (average four million subscribers are being added every month over the past six months). They prefer wireless service compared to wireline service, which is evident from the fact that while wireless subscriber base has increased 75 percent CAGR from 2001 to 2006, the wireline subscriber base growth rate has been negligible during the same period. In fact, many customers are returning their wireline phones to their service providers. The main drivers for this trend are quick service delivery for mobile connections, affordable pricing plans in the form of pre-paid cards and increased purchasing power among 18 to 40 years age group, prime market for this service.
Some of the positive impacts of this trend are as follows: According to a study, 18 percent mobile users are willing to change their handsets every year to newer models with more features, which is a good news for the handset vendors. The other impact is that while the operators have only limited options to generate additional revenues through value-added services from wireline service, the mobile operators have numerous options to generate non-voice revenues from their customers. Some examples of value-added services are ring tone download, ring back tone, talking SMS, mobisodes etc. Moreover, there exists great opportunity for content developers to develop applications suitable for mobile users like mobile gaming, location based services etc. On the negative side, there is increased threat of virus, spread through mobile data connections and Bluetooth technology, in the mobile phones making it unusable sometimes. This is good news for anti-virus solution providers who will gain from this trend. Moreover, according to the study conducted by international organization, prolonged mobile usage could lead to more health related issues, which is a bad news for heavy mobile users.
2. Telecom equipment manufacturing: The telecom equipment deployed in the Indian telecom network is primarily manufactured in other countries and exported to India. However, there is growing trend of telecom equipment manufacturing in India. Many equipment and handset vendors have either setup their manufacturing facilities or in process of setting up such facilities in India. The main drivers for this trend are availability of low cost & high quality human resources, favorable government policies encouraging investment in telecom manufacturing, and tender norms of telecom operators requiring the vendors to have local manufacturing facilities. Some of the positive impacts of this trend are as follows: Availability of local telecom hardware manufacturing will enable Indian companies to transform into new product innovators from being mere software solution developers. Moreover, with manufacturing factories and their supply chain in place in India, telecom equipment will become cheaper compared to being imported from other countries. Also, the operators could enjoy the benefits of quick turn around time for their telecom equipment repairs because EXIM procedure takes approximately 60 days to get the telecom equipment repaired abroad. Finally, the new telecom manufacturing facilities could lead to more economic development in those cities.
3. Managed Services: Usually, telecom service providers operate their network taking care of all activities like managing outside plant wiring and all the way up to total network management, on their own. However, there is a growing trend among the new operators, especially mobile operators, to outsource majority of their network operations to third party service providers. Typically, the complex network management work is outsourced to telecom equipment vendors. The main drivers for this trend are as follows: Since the new operators lack experience to manage their network efficiently, they need experts help to manage their network. This will help them to focus on their core competencies like marketing the telecom services to their customers. Moreover, in the competitive job environment, the employers find it difficult to manage the churning of their high-skilled manpower that is needed to manage the complex network. The major impacts of this trend are as follows: The outsourcing model will work efficiently when the network is simple or consists of network components from the same vendor. However, when the operator has complex network with the network elements from multiple vendors, end-to-end network management will be very difficult without active participation of operator, which means that the operators have to invest in developing in-house skills. The other impact of this trend is although the operator gets predicted operating expenses by outsourcing network operations, sometimes, that may not be the better deal for them compared to doing on their own. This is because when there are limited vendors for the outsourced activity like complex network management, the operators do not have flexibility to get better price from their vendors.
4. More revenues from copper base: Another major trend in the telecom industry is that the wireline operators want to extract more revenues out of their huge installed copper base (approximately 45 million homes are connected by wire) by introducing new services. The operators have deployed ADSL gear to offer broadband connections to the customers. Moreover, many telecom operators have signed deals with major enterprises to interconnect their offices creating VPN through their wireline network. Also, some telecom operators have started offering IPTV service in selected regions through ADSL lines. The major drivers for this trend are eroding revenues from wireline business due to competition from wireless and cable TV operators, technological advances like ADSL2+ and MPEG4-AVC enabling transmission of commercial quality video content at bandwidths supported by ADSL and increased demand of broadband connections with availability of low cost PCs. The major impact of this trend is the telecom operators have to increase their capex investments on their backbone network in the near future because the current backbone bandwidth is not enough for new services like video content distribution for their IPTV service. Moreover, the increased competition between telecom operators, cable TV operators in broadband access, and video content distribution will drive down the cost of various services benefiting Indian customers. The other positive impact is that the enterprises do not have build and maintain the VPN connecting their office networks through dedicated T1/E1 lines.
5. Drastic tariff reduction: Heavy competition in increasing customer base has forced the telecom operators to slash tariffs drastically especially for long distance calls. Many operators have introduced pricing plans with significant tariff reduction for their long distance traffic like 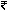 1 per minute for whole India, 40 paise per minute for same network calls etc. to attract more customers and to drive the call volume. This price cut is significant because till three years ago the long distance tariffs were as high as
1 per minute for whole India, 40 paise per minute for same network calls etc. to attract more customers and to drive the call volume. This price cut is significant because till three years ago the long distance tariffs were as high as 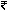 24 per minute for calls between certain regions of the country. The main drivers for this trend are as follows: The operators fear that they might experience customer base erosion once the features like Number portability and Carrier Access Code are implemented. Hence, they are introducing various pricing plans inducing the customers to stay within their network. Also, the telecom operators have to compete with VoIP operators who offer long distance calls service at very low prices through Internet. The major impact of this trend is that the operators likely to go for Softswitch deployments in their network to cut down their operational cost because they can not compete with VoIP operators through their TDM switches. Moreover, the steep reduction in long distance tariffs along with increased tele-density among the people could lead to the closure of STD booths in many parts of India except rural areas.
6. Increased Internet usage: Another important trend in the Indian telecom industry is the increased Internet usage among Indian customers. According to statistics, the number of Internet users in India stands at 39 million at the end of 2005 and estimated to reach 100 million in 2007. This is significant considering that only 3 million homes in India have personal computers. The study indicates that the Internet users spend their time primarily on email access, job search and online bank activities. The main drivers for this trend are increased awareness among public about internet, e-governance initiatives of government like setting up internet kiosks in villages & maintaining government information in their web pages to increase the internet usage and finally ubiquity of internet cafes from where majority of users access internet. The major impacts of the trend are as follows: Currently, most of the Internet search goes to U.S. websites due to non-availability of local content making the internet access slow and expensive. The problem can get only worse with the estimated steep increase in Internet user base. To relieve pressure on international bandwidth, it is possible that the telecom operators will partner with the content producers to develop more content relevant to Indian market. Another major opportunity that results from increased Internet usage in India is E-commerce, which is estimated to reach $500 million by 2007. The Internet users in India are comfortable in purchasing items online like garments, electronic items, train and flight tickets.
7. Enterprise communication through internet: There is growing trend of increased enterprise communication through public internet. Employees, who have to work away from their offices due to business or personal reasons, connect to their enterprise networks over public Internet using VPN. They use either wireless (WiFi) or wireline (ADSL) technologies to access the Internet. The main drivers for this trend are easy availability of Internet access points in homes (ADSL), hotel rooms (ADSL/WiFi) and airports (WiFi), and cost advantages in using VPN over Internet compared with dedicated access. The major impacts of this trend are as follows: Although, the employees use VPN software to connect to their company network over the internet in secured manner, their computers are still under the risk of attack from hackers at the internet access points especially at hotspots. However, this risk creates opportunity for the security software providers to develop solutions addressing this problem. The other impact is the need for increased range of coverage, maintaining the bandwidth, between the computer and the Internet access point for the business travelers in accessing Internet. Currently, the mobility of business travelers accessing the Internet is limited to small area served by hotspot. Two competing technologies WiMAX and 3G try to address this need through different mechanisms. It remains to be seen which technology will gain the market acceptance in addressing this requirement in the future.
Conclusion:
The trends in telecom industry have positive impacts on the operators, vendors and the end customers so far. However, with more technological changes and aggressive competition from other industries like cable TV, new trends having the potential to change the direction of telecom industry in either way could emerge in the future.
24 per minute for calls between certain regions of the country. The main drivers for this trend are as follows: The operators fear that they might experience customer base erosion once the features like Number portability and Carrier Access Code are implemented. Hence, they are introducing various pricing plans inducing the customers to stay within their network. Also, the telecom operators have to compete with VoIP operators who offer long distance calls service at very low prices through Internet. The major impact of this trend is that the operators likely to go for Softswitch deployments in their network to cut down their operational cost because they can not compete with VoIP operators through their TDM switches. Moreover, the steep reduction in long distance tariffs along with increased tele-density among the people could lead to the closure of STD booths in many parts of India except rural areas.
6. Increased Internet usage: Another important trend in the Indian telecom industry is the increased Internet usage among Indian customers. According to statistics, the number of Internet users in India stands at 39 million at the end of 2005 and estimated to reach 100 million in 2007. This is significant considering that only 3 million homes in India have personal computers. The study indicates that the Internet users spend their time primarily on email access, job search and online bank activities. The main drivers for this trend are increased awareness among public about internet, e-governance initiatives of government like setting up internet kiosks in villages & maintaining government information in their web pages to increase the internet usage and finally ubiquity of internet cafes from where majority of users access internet. The major impacts of the trend are as follows: Currently, most of the Internet search goes to U.S. websites due to non-availability of local content making the internet access slow and expensive. The problem can get only worse with the estimated steep increase in Internet user base. To relieve pressure on international bandwidth, it is possible that the telecom operators will partner with the content producers to develop more content relevant to Indian market. Another major opportunity that results from increased Internet usage in India is E-commerce, which is estimated to reach $500 million by 2007. The Internet users in India are comfortable in purchasing items online like garments, electronic items, train and flight tickets.
7. Enterprise communication through internet: There is growing trend of increased enterprise communication through public internet. Employees, who have to work away from their offices due to business or personal reasons, connect to their enterprise networks over public Internet using VPN. They use either wireless (WiFi) or wireline (ADSL) technologies to access the Internet. The main drivers for this trend are easy availability of Internet access points in homes (ADSL), hotel rooms (ADSL/WiFi) and airports (WiFi), and cost advantages in using VPN over Internet compared with dedicated access. The major impacts of this trend are as follows: Although, the employees use VPN software to connect to their company network over the internet in secured manner, their computers are still under the risk of attack from hackers at the internet access points especially at hotspots. However, this risk creates opportunity for the security software providers to develop solutions addressing this problem. The other impact is the need for increased range of coverage, maintaining the bandwidth, between the computer and the Internet access point for the business travelers in accessing Internet. Currently, the mobility of business travelers accessing the Internet is limited to small area served by hotspot. Two competing technologies WiMAX and 3G try to address this need through different mechanisms. It remains to be seen which technology will gain the market acceptance in addressing this requirement in the future.
Conclusion:
The trends in telecom industry have positive impacts on the operators, vendors and the end customers so far. However, with more technological changes and aggressive competition from other industries like cable TV, new trends having the potential to change the direction of telecom industry in either way could emerge in the future.
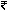 1 per minute for whole India, 40 paise per minute for same network calls etc. to attract more customers and to drive the call volume. This price cut is significant because till three years ago the long distance tariffs were as high as
1 per minute for whole India, 40 paise per minute for same network calls etc. to attract more customers and to drive the call volume. This price cut is significant because till three years ago the long distance tariffs were as high as 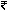 24 per minute for calls between certain regions of the country. The main drivers for this trend are as follows: The operators fear that they might experience customer base erosion once the features like Number portability and Carrier Access Code are implemented. Hence, they are introducing various pricing plans inducing the customers to stay within their network. Also, the telecom operators have to compete with VoIP operators who offer long distance calls service at very low prices through Internet. The major impact of this trend is that the operators likely to go for Softswitch deployments in their network to cut down their operational cost because they can not compete with VoIP operators through their TDM switches. Moreover, the steep reduction in long distance tariffs along with increased tele-density among the people could lead to the closure of STD booths in many parts of India except rural areas.
6. Increased Internet usage: Another important trend in the Indian telecom industry is the increased Internet usage among Indian customers. According to statistics, the number of Internet users in India stands at 39 million at the end of 2005 and estimated to reach 100 million in 2007. This is significant considering that only 3 million homes in India have personal computers. The study indicates that the Internet users spend their time primarily on email access, job search and online bank activities. The main drivers for this trend are increased awareness among public about internet, e-governance initiatives of government like setting up internet kiosks in villages & maintaining government information in their web pages to increase the internet usage and finally ubiquity of internet cafes from where majority of users access internet. The major impacts of the trend are as follows: Currently, most of the Internet search goes to U.S. websites due to non-availability of local content making the internet access slow and expensive. The problem can get only worse with the estimated steep increase in Internet user base. To relieve pressure on international bandwidth, it is possible that the telecom operators will partner with the content producers to develop more content relevant to Indian market. Another major opportunity that results from increased Internet usage in India is E-commerce, which is estimated to reach $500 million by 2007. The Internet users in India are comfortable in purchasing items online like garments, electronic items, train and flight tickets.
7. Enterprise communication through internet: There is growing trend of increased enterprise communication through public internet. Employees, who have to work away from their offices due to business or personal reasons, connect to their enterprise networks over public Internet using VPN. They use either wireless (WiFi) or wireline (ADSL) technologies to access the Internet. The main drivers for this trend are easy availability of Internet access points in homes (ADSL), hotel rooms (ADSL/WiFi) and airports (WiFi), and cost advantages in using VPN over Internet compared with dedicated access. The major impacts of this trend are as follows: Although, the employees use VPN software to connect to their company network over the internet in secured manner, their computers are still under the risk of attack from hackers at the internet access points especially at hotspots. However, this risk creates opportunity for the security software providers to develop solutions addressing this problem. The other impact is the need for increased range of coverage, maintaining the bandwidth, between the computer and the Internet access point for the business travelers in accessing Internet. Currently, the mobility of business travelers accessing the Internet is limited to small area served by hotspot. Two competing technologies WiMAX and 3G try to address this need through different mechanisms. It remains to be seen which technology will gain the market acceptance in addressing this requirement in the future.
Conclusion:
The trends in telecom industry have positive impacts on the operators, vendors and the end customers so far. However, with more technological changes and aggressive competition from other industries like cable TV, new trends having the potential to change the direction of telecom industry in either way could emerge in the future.
24 per minute for calls between certain regions of the country. The main drivers for this trend are as follows: The operators fear that they might experience customer base erosion once the features like Number portability and Carrier Access Code are implemented. Hence, they are introducing various pricing plans inducing the customers to stay within their network. Also, the telecom operators have to compete with VoIP operators who offer long distance calls service at very low prices through Internet. The major impact of this trend is that the operators likely to go for Softswitch deployments in their network to cut down their operational cost because they can not compete with VoIP operators through their TDM switches. Moreover, the steep reduction in long distance tariffs along with increased tele-density among the people could lead to the closure of STD booths in many parts of India except rural areas.
6. Increased Internet usage: Another important trend in the Indian telecom industry is the increased Internet usage among Indian customers. According to statistics, the number of Internet users in India stands at 39 million at the end of 2005 and estimated to reach 100 million in 2007. This is significant considering that only 3 million homes in India have personal computers. The study indicates that the Internet users spend their time primarily on email access, job search and online bank activities. The main drivers for this trend are increased awareness among public about internet, e-governance initiatives of government like setting up internet kiosks in villages & maintaining government information in their web pages to increase the internet usage and finally ubiquity of internet cafes from where majority of users access internet. The major impacts of the trend are as follows: Currently, most of the Internet search goes to U.S. websites due to non-availability of local content making the internet access slow and expensive. The problem can get only worse with the estimated steep increase in Internet user base. To relieve pressure on international bandwidth, it is possible that the telecom operators will partner with the content producers to develop more content relevant to Indian market. Another major opportunity that results from increased Internet usage in India is E-commerce, which is estimated to reach $500 million by 2007. The Internet users in India are comfortable in purchasing items online like garments, electronic items, train and flight tickets.
7. Enterprise communication through internet: There is growing trend of increased enterprise communication through public internet. Employees, who have to work away from their offices due to business or personal reasons, connect to their enterprise networks over public Internet using VPN. They use either wireless (WiFi) or wireline (ADSL) technologies to access the Internet. The main drivers for this trend are easy availability of Internet access points in homes (ADSL), hotel rooms (ADSL/WiFi) and airports (WiFi), and cost advantages in using VPN over Internet compared with dedicated access. The major impacts of this trend are as follows: Although, the employees use VPN software to connect to their company network over the internet in secured manner, their computers are still under the risk of attack from hackers at the internet access points especially at hotspots. However, this risk creates opportunity for the security software providers to develop solutions addressing this problem. The other impact is the need for increased range of coverage, maintaining the bandwidth, between the computer and the Internet access point for the business travelers in accessing Internet. Currently, the mobility of business travelers accessing the Internet is limited to small area served by hotspot. Two competing technologies WiMAX and 3G try to address this need through different mechanisms. It remains to be seen which technology will gain the market acceptance in addressing this requirement in the future.
Conclusion:
The trends in telecom industry have positive impacts on the operators, vendors and the end customers so far. However, with more technological changes and aggressive competition from other industries like cable TV, new trends having the potential to change the direction of telecom industry in either way could emerge in the future.