News >> >>
Now, MBAs to become clerks
By siliconindia
|
Thursday, 12 November 2009, 21:53 IST |
6 Comments
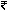 8,000 a month job are engineers and MBAs, though the job specified only Class 12 as minimum qualification criterion.
The server of State Bank of India crashed last year when two million candidates applied for 20,000 clerical posts. The written examination had to be conducted over four shifts as the bank just could not find enough venues where the tests could be held. A year on, the country's largest bank faces an even bigger dilemma. It has 11,000 clerical posts on offer, but has received 3.4 million applications. That's about 300 applications for every vacancy, reports Rediff.com.
SBI is conducting the entrance test on three Sundays, in two sessions (morning and afternoon) across 83 centres. The exercise is estimated to cost at least
8,000 a month job are engineers and MBAs, though the job specified only Class 12 as minimum qualification criterion.
The server of State Bank of India crashed last year when two million candidates applied for 20,000 clerical posts. The written examination had to be conducted over four shifts as the bank just could not find enough venues where the tests could be held. A year on, the country's largest bank faces an even bigger dilemma. It has 11,000 clerical posts on offer, but has received 3.4 million applications. That's about 300 applications for every vacancy, reports Rediff.com.
SBI is conducting the entrance test on three Sundays, in two sessions (morning and afternoon) across 83 centres. The exercise is estimated to cost at least 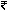 65 crore (
65 crore (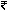 650 million), which will be taken care of by the money obtained from application fees. SBI needs the clerks for its ambitious branch expansion program.
The bank can afford the luxury of being extremely choosy - a vast majority of the candidates who have applied for the
650 million), which will be taken care of by the money obtained from application fees. SBI needs the clerks for its ambitious branch expansion program.
The bank can afford the luxury of being extremely choosy - a vast majority of the candidates who have applied for the 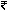 8,000 a month job are engineering graduates and MBAs, even though the job specified only Class 12 as minimum qualification criterion.
It's not that there aren't enough suitable jobs for good-quality engineers and MBAs. There are countless stories of how leading Indian companies are visiting engineering and MBA colleges in interior parts of the country to add to their basket of employable graduates but are returning empty-handed.
The main problem is that of employability. Studies have indicated that only one in four graduates from India's colleges is employable. A Nasscom study found that India still produces plenty of engineers - 400,000 a year. But most are deficient in the required technical skills, fluency in English or ability to work in a team and deliver basic oral presentations.
As a result, those engineers or MBAs who manage to become SBI clerks may still consider themselves lucky. Sandip Mukherjee, an engineering graduate from one of the middle-rung private institutes in Kolkata came to Navi Mumbai to join a windmill company which has its headquarters in Europe. The quality of the job, however, he says, was only slightly better than that of a security guard. Mukherjee, who was lucky enough to find another job within four months, says his ex-boss had asked him to prepare a project report on the security system in the company's godowns.
Apparently, the company suspected that a lot of pilferage was taking place in one of its godowns. The engineer was asked to station himself in the security office to figure out the lacunae in the system. One of his observations was that some people left the godown unchecked during lunch hour when the security guard would go to the canteen to bring food. Impressed with this finding, the boss then asked him to find out whether this was happening during tea break or at dinner time also, or whether the security guards went to the toilet often, leaving the gate unmanned. "I didn't pursue engineering to observe people's tea and toilet habits," Mukherjee wrote in his resignation letter.
Companies say that this mismatch between qualification and quality of job is inevitable in a country where everybody and his uncle is either an engineer or an MBA. The quality of teaching in most of the second-rung institutes is poor and companies often have to pay through the nose to train them.
Indian Institute of Technology alumni have repeatedly expressed serious concern over the mushrooming of engineering colleges that are being run as 'business ventures' by contractors, builders, coal dealers, brick-kiln owners and sweetmeat sellers.
In Uttar Pradesh alone, 250 such engineering colleges have come up in the last decade with an intake of about 60,000 students. India's vocational training institutes produce six million students every year. That's a minuscule number considering that an estimated 88.5 million people in the 15-29 age group need such training. Industry people says less than half of the six million people who have received vocational training are in the employable category.
A Planning Commission assessment shows 80 percent of the 12.8 million new entrants to India's workforce every year have no opportunity for skills training. Even more worrying is the fact that only two percent of the workforce has skills training and 80 per cent of the rural and urban workforce does not possess any 'identifiable' market skills.
8,000 a month job are engineering graduates and MBAs, even though the job specified only Class 12 as minimum qualification criterion.
It's not that there aren't enough suitable jobs for good-quality engineers and MBAs. There are countless stories of how leading Indian companies are visiting engineering and MBA colleges in interior parts of the country to add to their basket of employable graduates but are returning empty-handed.
The main problem is that of employability. Studies have indicated that only one in four graduates from India's colleges is employable. A Nasscom study found that India still produces plenty of engineers - 400,000 a year. But most are deficient in the required technical skills, fluency in English or ability to work in a team and deliver basic oral presentations.
As a result, those engineers or MBAs who manage to become SBI clerks may still consider themselves lucky. Sandip Mukherjee, an engineering graduate from one of the middle-rung private institutes in Kolkata came to Navi Mumbai to join a windmill company which has its headquarters in Europe. The quality of the job, however, he says, was only slightly better than that of a security guard. Mukherjee, who was lucky enough to find another job within four months, says his ex-boss had asked him to prepare a project report on the security system in the company's godowns.
Apparently, the company suspected that a lot of pilferage was taking place in one of its godowns. The engineer was asked to station himself in the security office to figure out the lacunae in the system. One of his observations was that some people left the godown unchecked during lunch hour when the security guard would go to the canteen to bring food. Impressed with this finding, the boss then asked him to find out whether this was happening during tea break or at dinner time also, or whether the security guards went to the toilet often, leaving the gate unmanned. "I didn't pursue engineering to observe people's tea and toilet habits," Mukherjee wrote in his resignation letter.
Companies say that this mismatch between qualification and quality of job is inevitable in a country where everybody and his uncle is either an engineer or an MBA. The quality of teaching in most of the second-rung institutes is poor and companies often have to pay through the nose to train them.
Indian Institute of Technology alumni have repeatedly expressed serious concern over the mushrooming of engineering colleges that are being run as 'business ventures' by contractors, builders, coal dealers, brick-kiln owners and sweetmeat sellers.
In Uttar Pradesh alone, 250 such engineering colleges have come up in the last decade with an intake of about 60,000 students. India's vocational training institutes produce six million students every year. That's a minuscule number considering that an estimated 88.5 million people in the 15-29 age group need such training. Industry people says less than half of the six million people who have received vocational training are in the employable category.
A Planning Commission assessment shows 80 percent of the 12.8 million new entrants to India's workforce every year have no opportunity for skills training. Even more worrying is the fact that only two percent of the workforce has skills training and 80 per cent of the rural and urban workforce does not possess any 'identifiable' market skills.